
Why HEPA Filter’s Leakage Test is More Important Than the Filter Itself ?
Why HEPA Filter’s Leakage Test is More Important Than the Filter Itself ?
In pharmaceutical factories, HEPA filter (filters) are the last line of defense in the purification system. The integrity and leak-free performance of their installation are fundamental to ensuring that the clean area environment meets the requirements. Therefore, replacing a new filter is far from enough. According to the international standard ISO 14644-3:2019 (Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments - Part 3: Test methods) and the GMP regulations of various countries, a HEPA Filter’s Leakage Test which must be performed in the following situations:
① After installing new filters
② After any adjustment or reinstallation of the filter or its sealing components
③ Regular revalidation, usually every 6 or 12 months

What is a HEPA Filter?
Definition: The end (terminal) filtration of the purification system is the most critical component to ensure air cleanliness.
Function: Filters particles ≥0.3μm (or 0.5μm) with filtration efficiencies of 99.97% to 99.995% (for 0.3μm particles). This filter effectively removes contaminants such as bacteria and viral vectors, making it essential for achieving Class A and Class B cleanroom requirements.
Structural features: Glass fiber filter paper is used as the filter material, and the outer frame is mostly made of wood, aluminum alloy or stainless steel. The structure must be very tight to ensure no leakage.
Installation and Replacement: The filters installed at the end of the air outlet. an on-site scanning leak test (DOP/PAO test) is required between the mounting frame to ensure a leak-free seal. Once installed, it cannot be cleaned and can only be replaced. The service life is generally 2-5 years.
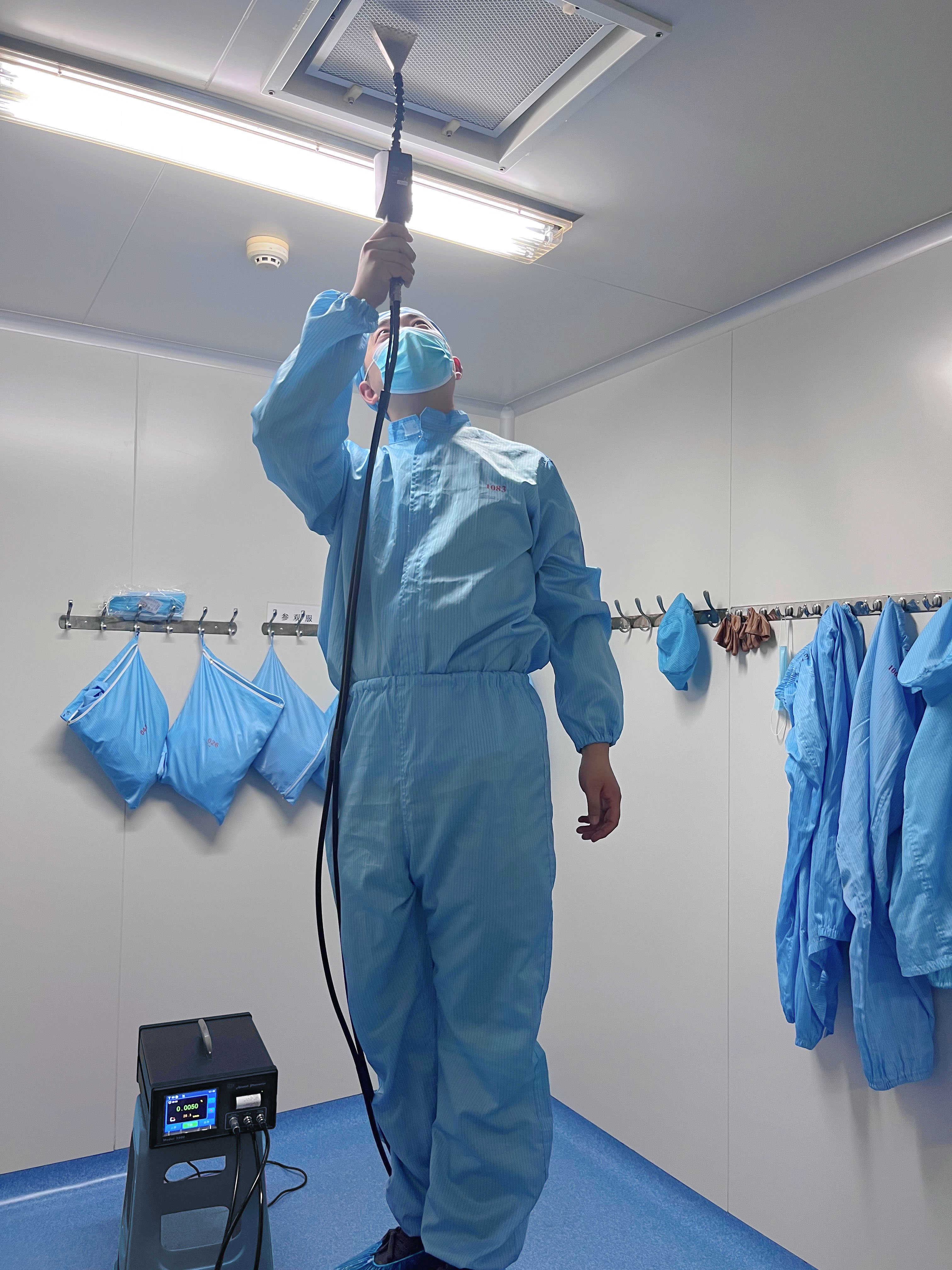
Replacement and Leak Detection of HEPA Filters (DOP/PAO test)
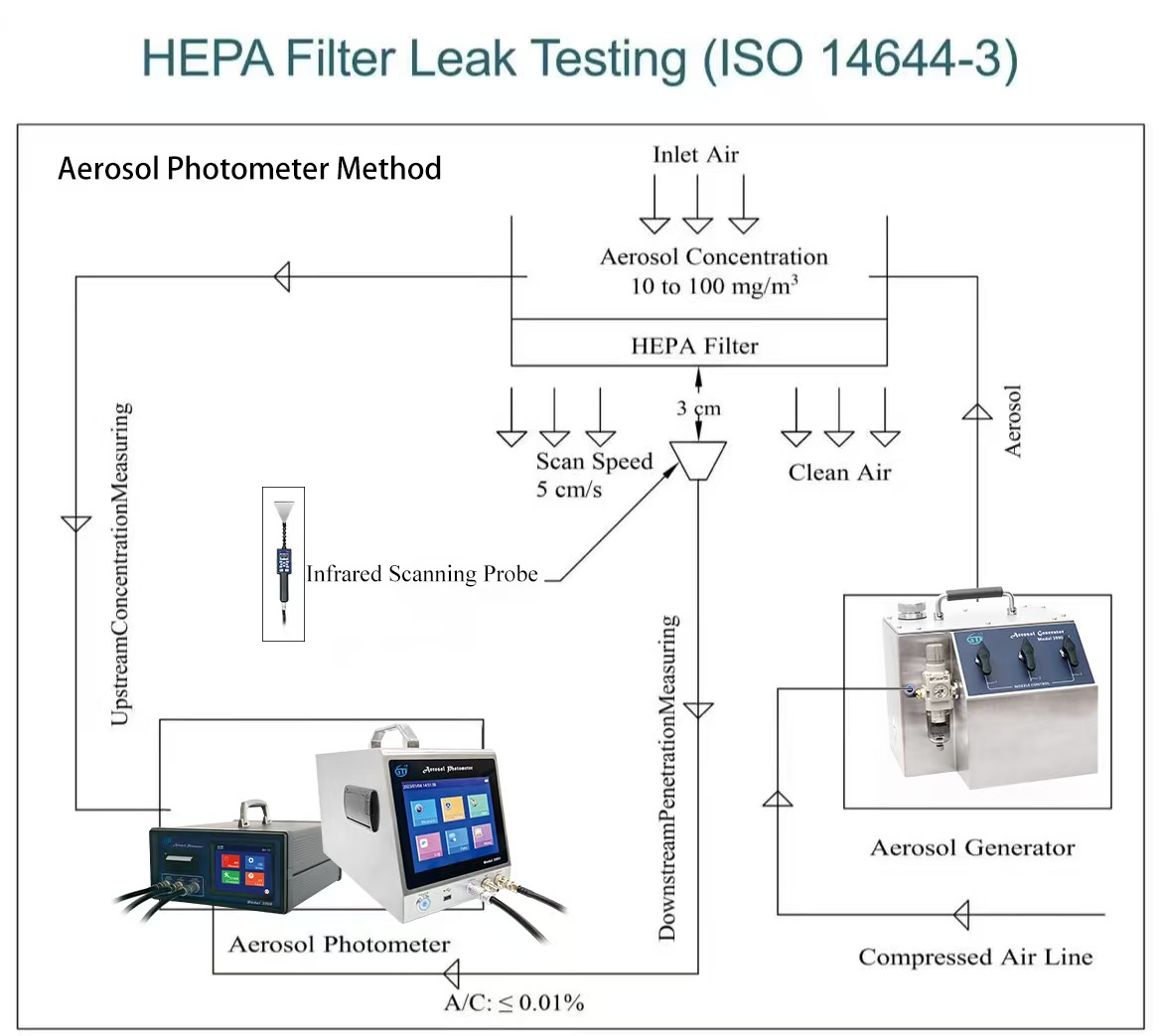
The leak test of HEPA filters usually adopts the Aerosol Photometer Scanning Method, and its key process is as follows:
Upstream aerosol generation: A high concentration of PAO (polyalphaolefin) or DOP (dioctyl phthalate) aerosol is uniformly generated on the air inlet side (upstream) of the HEPA filter through a dedicated device as the challenge substance.
Downstream scanning: On the outlet side (downstream) of the HEPA filter, the test requires
using the sampling probe of the aerosol photometer to perform a uniform, overlapping, and exhaustive scan of the entire cross-section of the filter, the seal between the filter and the mounting frame, and all possible leak points in the static pressure box at a very close distance (usually 2-3 cm from the filter surface).
Result determination: The photometer reads and displays the downstream aerosol concentration in real time. Any point where the leakage rate (ratio of downstream concentration to upstream concentration) exceeds 0.01% (i.e., above 99.99% efficiency) is considered unacceptable. For any unacceptable point, the filter must be repaired (special sealants are available for minor leaks) or replaced and retested until it passes.
This test is a mandatory verification item in the quality system of pharmaceutical companies. Its purpose is not only to confirm that the filter itself is free of defects, but also to confirm the reliability of the filter installation and seal, thereby ensuring the safety, effectiveness and compliance of the pharmaceutical production environment from the most technical level.
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)









