GTI Products Line for HEPA Filter Leakage Testing
Main Steps of HEPA Filter Integrity Testing

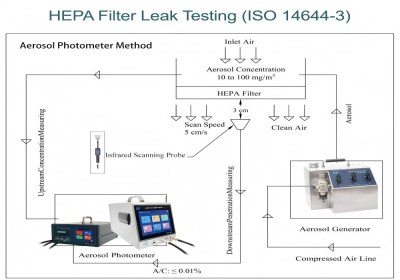
Ⅰ. Standard Procedure for HEPA Filter Leakage Testing
The leakage testing for HEPA filter is systematical. It needs to obey a standard procedure strictly, so that can ensure the accuracy and reliability of testing results.
² Introduction of Aerosol
It is an essential step to introduce PAO into the upstream of HEPA filters. According to different applications, the ways to aerosol introduction are different.
² HEPA filters in the HVAC systems:
To make sure the aerosol concentration equably when it reaches the HEPA filter, the aerosol is introduced from the negative pressure side of the fan. If it’s leaded into from the air tube, the lead-in point should be installed at least 10 times the duct diameter away from the HEPA filter; and minimize pipe bends (according to the America environment science and technical association). In practice, it is sufficient to keep the upstream aerosol concentration within the required range.
² HEPA filters in laminar flow hood or ultra-clean table:
Leakage testing of this kind equipment is relatively simple — aerosol can be directly lead from the negative pressure side of the fan. There is no need to consider the problem of uneven concentration caused by long-distance transportation.
² Preparation of Testing Equipment
Initialization and calibration of aerosol photometers are crucial steps in ensuring detection accuracy:
Perform the initialization procedure according to the equipment operation manual.
Configure alarm thresholds (usually set to 0.01% leakage rate)
Connect the UPSTREAM sampling tube to the upstream sampling port.
Measure and adjust the upstream aerosol concentration to the ideal range of 10~20 μg/mL.
Attention needs to be paid to the operation procedures of the aerosol generator during this stage. It should be ensured that the particle size distribution of aerosol meets the test requirements.
² Operation of Scanning
Scanning is the core step in the leakage testing. It must be strictly followed in accordance with the following operating procedures:
Preparation: Remove the HEPA diffuser to expose the entire filter surface and surrounding seals. The scanning area should include: the filter face, all seals between the filter and the frame, between frames, and between the frame and the pressure chamber.
² Scanning parameter:
The scanning probe should be kept approximately 3 cm away from the filter surface.
Scanning speed should be controlled within 5cm/s
The scanning path is linear reciprocation
Adjacent scanning lines should be properly overlapped (50% of the diameter of the scanning probe).
² Leakage detection:
When the testing instrument alarms (LEAKAGE exceeds the 0.01%), it indicates a leakage at that location. Then mark it, and use silicone sealant for temporary sealing or tightening. Then rescan to confirm the repair effect.
² Safety protection:
Operators must wear protective face masks and goggles at all times to prevent inhaling or touching aerosols. Additionally, the stability of upstream aerosol concentrations should be checked periodically. The complete test of each filter typically takes approximately 5 minutes.
Ⅱ. Judgment and Handle for Testing Results
There are clear standards and procedures for judging the results of HEPA filter leakage testing to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the filtration system.
² Standard of Qualification
The acceptable leakage rate for HEPA filters is ≤0.01%. The concrete rules are as follow:
² Judgment for qualification:
If the leakage rate at all test points does not exceed 0.01% during the HEPA filter testing, the filter is deemed qualified and can continue to be used.
² Judgment for disqualification:
If the leakage rate at any point exceeds 0.01%, the filter is deemed unqualified and immediate corrective action must be taken.
² Handle for Leakage
For unqualified filters, the following procedures can be followed:
² Mark the leakage:
Use non-removable markers to accurately mark all leaks and record the leakage rate.
² Standards for repair:
Specialized adhesive can be used to repair leaks in the filter media.
The repair area for a single leak must not exceed 1% of the whole filter area.
The total repair area for all leaks must not exceed 5% of the whole area.
If any of the above standards dose not meet, the entire filter must be replaced.
² Re-inspection requirements:
After all repairs are completed, a full scan and leak detection must be performed again to ensure that there is no leaks in these areas, and that the overall leakage rate meets the standards.
Ⅲ. Suggestions for HEPA Filter Leakage Testing Cycle
Different organizations and standards have different recommendations for HEPA filter leakage testing cycle. Users should choose the appropriate testing frequency based on their own industry characteristics.
Eg, in the Guidance for FDA Sterile Drug Manufacture, the recommended cycle is once half a year.
In addition to the regular inspections mentioned above, the leakage testing is also required in the following special situations:
²After installation or replacement:
All newly installed or replaced HEPA filters should be immediately completed leakage testing to confirm installation quality.
²Abnormal situation:
Environmental monitoring shows that air quality has deteriorated abnormally.
The product failed the sterility test.
Culture medium simulated filling test failed.
To be a component of the deviation survey.
²Special equipment: HEPA filters used in equipment, such as drying tunnels and drying ovens, should also be done with the leakage testing. For their testing cycle can refer to the main system standard.
Ⅳ. Analysis for Unqualified HEPA Filters
HEPA filters may fail to meet standards during factory testing or on-site leakage testing. The reasons can be summarized as follows:
²Visually Identifiable Reasons
Problems that can be identified through visual inspection or simple testing:
Damage on filter surface:
Obvious or mechanical damage, which is easy to observe with the naked eye.
Minor damage, which can be found by the test bench detection
Several damage can be required professionally in the plant.
Damage during production:
The filter material is subjected to excessive stress during manufacturing.
Accidental damage caused by improper human operation.
Localized damage of filters is repairable, but must meet standard requirements.
Sealing defects:
Air leakage at the junction of the filter and the filter frame (the most common cause of disqualification).
Air leakage caused by improper sealing of sealant joints.
[Solutions]
Using on-site foamed polyurethane sealing strips can avoid joint problems.
Adhesive strips with joints should adopt a labyrinth-type interface design.
²Raw Material Reasons
Defects related to the quality of filter material:
Insufficient filter material efficiency:
The HEPA filter material does not meet the standards (filtration efficiency of ≥99.97% for 0.3μm particles at an air velocity of 5.3cm/s).
Fundamental defects cannot be fixed through post-processing.
Material dust generation:
Traditional diaphragm filters have poor control over the raw materials used for paper diaphragms.
Insufficient cleanliness in the filter material production environment leads to the presence of dust.
Some testing methods are unable to detect the reasons for these potential dust generation.
Detection Process Problems:
Misjudgment caused by improper testing methods or operations:
Vortex interference:
During scanning, the vortex at the air outlet carries surrounding dust into the scanning area.
It is difficult to distinguish between real leakage and false positives caused by vortex interference.
[Solution]
Manufacturers solve this problem by installing inspection stations in cleanrooms.
Downstream concentration misjudgment:
After installation, filter performance should not be judged solely based on downstream dust concentration.
Qualified filters may be misjudged due to other sources of contamination.
Solution: A comprehensive judgment requires combining multi-point detection and trend analysis.
Ⅴ. Summary and Suggestion
HEPA filter leakage testing is a crucial step in ensuring air quality in clean environments, and it requires the establishment of a systematic testing and maintenance plan:
²Standardization of process: Follow the detection process strictly — every part needs standardized operation from aerosol introduction to scanning.
²Rationalization of cycle: The testing frequency should be determined based on industry standards and actual needs. It is recommended to shorten the testing interval in a sterile environment.
²Judgment of Results: Correctly distinguish between real and false leaks. A combination of methods is used to comprehensively assess the filter status.
²Trace of Problems: When leaks are found, the root cause should be analyzed from multiple aspects such as materials, manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
²Completeness of Recording: Record detailed data and problems found in each leak testing, and establish a filter lifecycle profile.
Systematic leakage testing management will ensure that HEPA filters are in optimal working condition, also provide reliable protection for the clean environment. If you have any needs regarding HEPA filter leakage testing, please contact GTI for related testing equipment.
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)